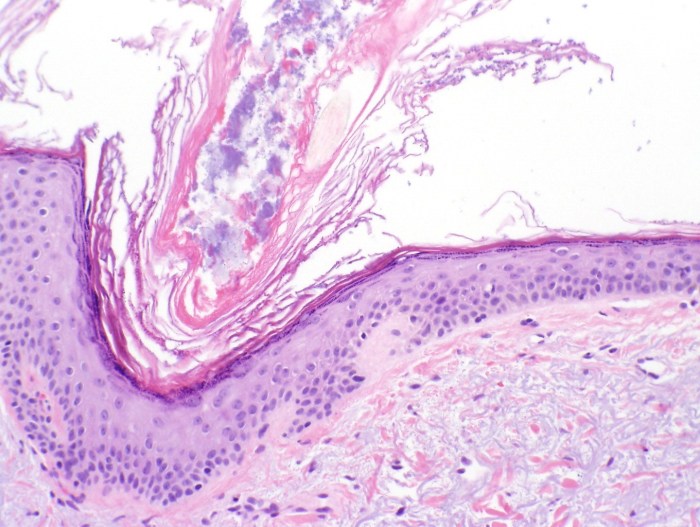
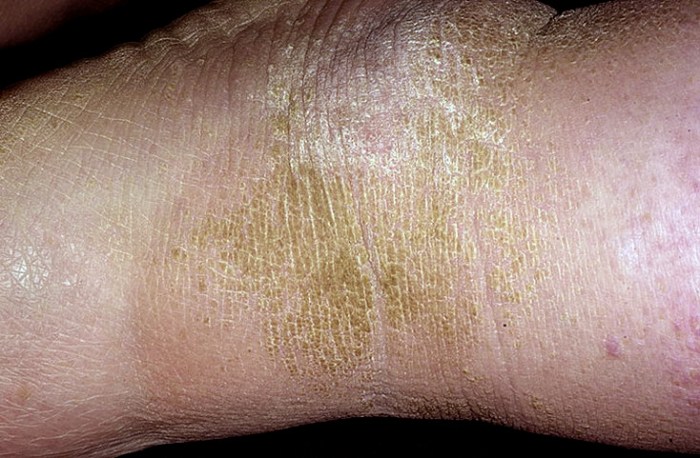
Retention hyperkeratosis is the hereditary tendency for acne-prone skin to – Retention hyperkeratosis, the hereditary tendency for acne-prone skin, is a prevalent dermatological condition that affects a significant proportion of the population. This article delves into the intricacies of retention hyperkeratosis, exploring its genetic basis, pathophysiology, clinical manifestations, differential diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures.
By understanding the underlying mechanisms and available management strategies, healthcare professionals can effectively address this common skin concern and improve patient outcomes.
Retention hyperkeratosis arises from a combination of genetic predisposition and environmental factors, leading to impaired desquamation and excessive keratinization within the pilosebaceous unit. This abnormal process results in the formation of comedones, papules, and pustules, which are the characteristic lesions of acne-prone skin.
1. Retention Hyperkeratosis
Hereditary Tendency for Acne-Prone Skin
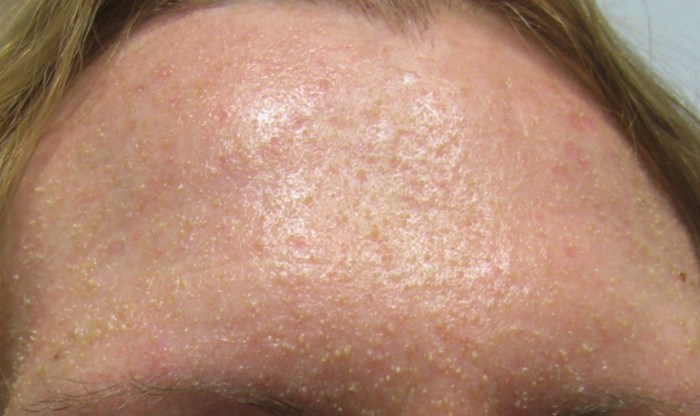
Retention hyperkeratosis is a genetic condition that affects the skin’s ability to shed dead skin cells. This leads to the formation of comedones, which are the primary lesions of acne.
Retention hyperkeratosis is caused by mutations in the genes that encode for proteins involved in skin cell differentiation and desquamation. These mutations lead to the production of abnormal keratin proteins, which accumulate in the hair follicles and cause them to become clogged.
2. Pathophysiology of Retention Hyperkeratosis
The pathophysiology of retention hyperkeratosis is complex and involves several cellular and molecular mechanisms. The primary defect is in the process of desquamation, which is the shedding of dead skin cells from the surface of the skin.
In individuals with retention hyperkeratosis, desquamation is impaired due to the accumulation of abnormal keratin proteins in the hair follicles. This leads to the formation of comedones, which are small, black or white bumps that are filled with sebum and dead skin cells.
3. Clinical Manifestations of Retention Hyperkeratosis
The clinical manifestations of retention hyperkeratosis are primarily characterized by the presence of comedones. Comedones can be either open (blackheads) or closed (whiteheads). They are typically located on the face, chest, and back.
In addition to comedones, individuals with retention hyperkeratosis may also develop papules, pustules, and nodules. These lesions are typically inflamed and can be painful.
4. Differential Diagnosis of Retention Hyperkeratosis, Retention hyperkeratosis is the hereditary tendency for acne-prone skin to
The differential diagnosis of retention hyperkeratosis includes a number of other skin conditions that can cause similar clinical manifestations. These conditions include:
- Acne vulgaris
- Rosacea
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- Perioral dermatitis
It is important to distinguish between retention hyperkeratosis and these other conditions in order to ensure appropriate treatment.
5. Treatment Options for Retention Hyperkeratosis
The treatment of retention hyperkeratosis typically involves the use of topical medications that help to reduce the production of keratin and improve desquamation. These medications include:
- Retinoids
- Salicylic acid
- Benzoyl peroxide
In some cases, oral medications may also be necessary to control the inflammation associated with retention hyperkeratosis.
6. Prevention and Management of Retention Hyperkeratosis
There is no cure for retention hyperkeratosis, but there are a number of things that can be done to prevent and manage the condition. These include:
- Using gentle cleansers and moisturizers
- Avoiding harsh scrubs and exfoliants
- Protecting the skin from the sun
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting regular exercise
By following these tips, individuals with retention hyperkeratosis can help to reduce the severity of their symptoms and improve their overall skin health.
FAQ Overview: Retention Hyperkeratosis Is The Hereditary Tendency For Acne-prone Skin To
What causes retention hyperkeratosis?
Retention hyperkeratosis is caused by a combination of genetic factors and environmental triggers that lead to impaired desquamation and excessive keratinization.
What are the common symptoms of retention hyperkeratosis?
The most common symptoms of retention hyperkeratosis are comedones (blackheads and whiteheads), papules (small, red bumps), and pustules (pus-filled bumps).
How is retention hyperkeratosis treated?
Treatment options for retention hyperkeratosis include topical retinoids, antibiotics, chemical peels, and lifestyle modifications.
Can retention hyperkeratosis be prevented?
While retention hyperkeratosis has a genetic component, following a proper skincare routine, avoiding harsh chemicals, and managing stress can help prevent or reduce the severity of symptoms.