Lab 3-4 reviewing motherboard documentation – Embarking on Lab 3-4: Reviewing Motherboard Documentation, we delve into the intricacies of this fundamental component, exploring its anatomy, specifications, form factors, installation, troubleshooting, and maintenance. With each section, we unravel the complexities of motherboards, empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and navigate the technological landscape with confidence.
Motherboard Components
A motherboard is the main circuit board of a computer. It connects all the essential components of a computer, including the CPU, memory, storage, and expansion cards. The motherboard also provides power to these components.
The following is a diagram of a motherboard:
[Diagram of a motherboard with key components labeled]
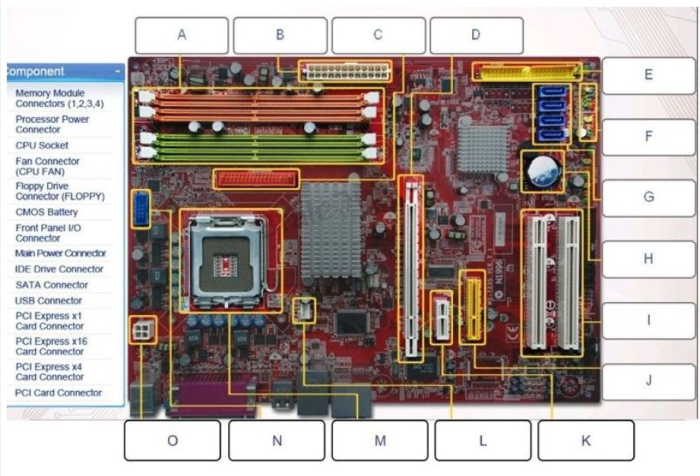
The key components of a motherboard include:
- CPU socket: This is where the CPU is installed.
- Memory slots: These are where the memory modules are installed.
- Storage connectors: These are where the storage devices are connected.
- Expansion slots: These are where expansion cards are installed.
- Power connectors: These are where the power supply is connected.
- BIOS chip: This is the firmware that controls the motherboard.
Motherboard Specifications
When choosing a motherboard, it is important to consider the following specifications:
- Socket type: This determines which CPUs are compatible with the motherboard.
- Memory type: This determines which type of memory modules are compatible with the motherboard.
- Storage connectors: This determines which type of storage devices are compatible with the motherboard.
- Expansion slots: This determines which type of expansion cards are compatible with the motherboard.
- Form factor: This determines the size and shape of the motherboard.
The following is an example of a motherboard specification:
Socket type: LGA 1200
Memory type: DDR4
Storage connectors: SATA 3, M.2
Expansion slots: PCIe 3.0 x16, PCIe 3.0 x4
Form factor: ATX
Motherboard Form Factors

The following are the different motherboard form factors available:
- ATX: This is the most common motherboard form factor. It is large and rectangular, and it has a standard set of mounting holes.
- Micro ATX: This is a smaller version of the ATX form factor. It is less common, but it is still compatible with most cases.
- Mini ITX: This is the smallest motherboard form factor. It is designed for small cases, and it has a limited number of expansion slots.
The following is a table comparing the different motherboard form factors:
| Form factor | Size | Mounting holes | Expansion slots |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATX | 12 inches x 9.6 inches | Standard | 7 |
| Micro ATX | 9.6 inches x 9.6 inches | Standard | 4 |
| Mini ITX | 6.7 inches x 6.7 inches | Limited | 1 |
Motherboard Installation

To install a motherboard, follow these steps:
- Open the case and remove the old motherboard.
- Place the new motherboard in the case and align it with the mounting holes.
- Secure the motherboard to the case with screws.
- Install the CPU in the socket.
- Install the memory modules in the slots.
- Install the storage devices in the connectors.
- Install the expansion cards in the slots.
- Connect the power supply to the motherboard.
- Close the case and power on the computer.
Motherboard Troubleshooting

The following are some common motherboard problems and their potential causes:
| Problem | Potential cause |
|---|---|
| Computer does not power on | Power supply failure, motherboard failure, CPU failure |
| Computer beeps and does not boot | Memory failure, graphics card failure, motherboard failure |
| Computer boots but does not display anything on the monitor | Graphics card failure, monitor failure, motherboard failure |
| Computer freezes randomly | Overheating, memory failure, motherboard failure |
| Computer crashes when running certain programs | Software incompatibility, hardware failure, motherboard failure |
Motherboard Maintenance
To maintain a motherboard, follow these tips:
- Keep the motherboard clean and free of dust.
- Do not overclock the motherboard.
- Do not expose the motherboard to extreme temperatures.
- Handle the motherboard with care.
- Update the motherboard BIOS regularly.
Detailed FAQs: Lab 3-4 Reviewing Motherboard Documentation
What is the purpose of a motherboard?
A motherboard is the central component of a computer system that connects all the essential components, including the processor, memory, storage, and expansion cards.
What are the key specifications to consider when choosing a motherboard?
When selecting a motherboard, it is important to consider factors such as the socket type, supported memory type and capacity, expansion slots, and connectivity options.
What are the different motherboard form factors?
Common motherboard form factors include ATX, micro ATX, mini ITX, and E-ATX, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of size, expansion capabilities, and compatibility.
How do I troubleshoot common motherboard problems?
Troubleshooting motherboard issues can involve checking for loose connections, updating BIOS, resetting CMOS, or replacing faulty components.
What are best practices for maintaining a motherboard?
To ensure optimal performance and longevity, it is recommended to keep the motherboard clean, avoid electrostatic discharge, and handle it with care during installation and maintenance.