Proteins and nucleic acids venn diagram, the centerpiece of this discourse, unveils the intricate connections between the fundamental building blocks of life. These macromolecules, with their diverse structures and functions, orchestrate a symphony of cellular processes that govern the very essence of living organisms.
Delving into the depths of their shared characteristics, we uncover the common threads that unite these molecules. Yet, it is in their functional roles that we witness the true extent of their interdependence, as proteins and nucleic acids engage in a delicate dance to maintain the integrity and perpetuate the continuity of life.
Proteins and Nucleic Acids: Shared Characteristics
Proteins and nucleic acids are two essential biomolecules that play crucial roles in all living organisms. They share several common characteristics that contribute to their biological functions.
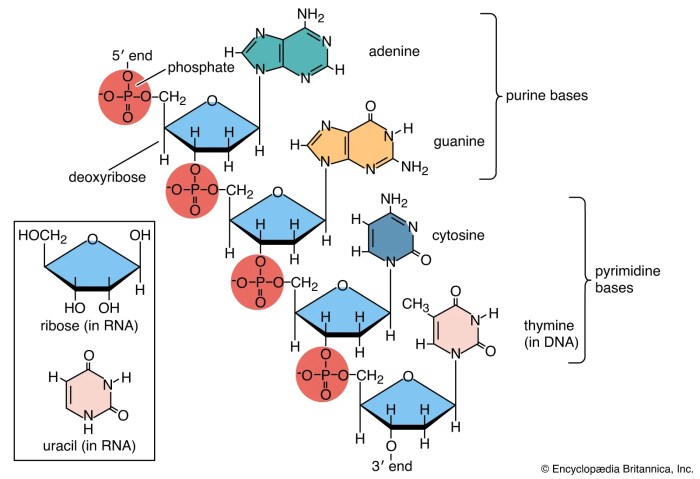
Both proteins and nucleic acids are composed of repeating subunits called monomers. In proteins, the monomers are amino acids, while in nucleic acids, they are nucleotides. These monomers are linked together by covalent bonds to form polymers. Proteins have a linear structure, while nucleic acids can have either a linear or branched structure.
The sequence of monomers in proteins and nucleic acids determines their unique properties and functions. Proteins exhibit a wide range of structures, including fibrous, globular, and membrane-bound proteins. Nucleic acids can be single-stranded or double-stranded, and they can form various secondary and tertiary structures.
Functional Roles of Proteins and Nucleic Acids
Proteins perform a vast array of functions in biological systems. They act as enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions, as structural components that provide support and shape to cells, and as signaling molecules that transmit information within and between cells.
Nucleic acids, primarily DNA and RNA, play a central role in storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA contains the instructions for all the proteins that an organism can produce. RNA molecules are involved in protein synthesis, carrying the genetic code from DNA to the ribosomes where proteins are assembled.
Proteins and nucleic acids interact to carry out essential cellular processes. For example, proteins bind to DNA to regulate gene expression, and RNA molecules act as templates for protein synthesis.
Protein-Nucleic Acid Interactions
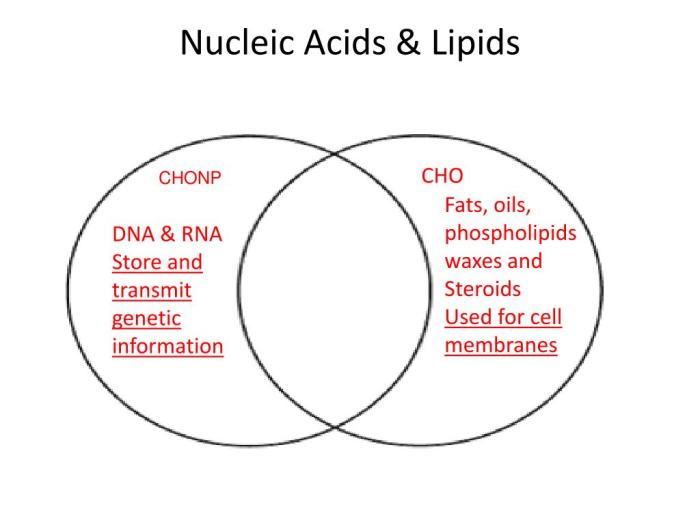
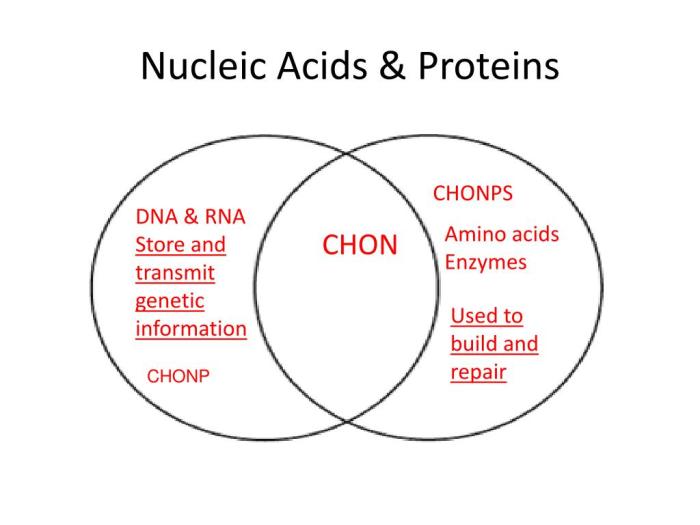
The overlapping functions of proteins and nucleic acids are illustrated in the following Venn diagram:
- Storage and transmission of genetic information
- Regulation of gene expression
- Protein synthesis
- Enzymes
- Structural components
- Signaling molecules
- Storage of genetic information
- Transmission of genetic information
- Template for protein synthesis
Proteins bind to nucleic acids through various mechanisms, including hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, and hydrophobic interactions. These interactions allow proteins to regulate gene expression by controlling the accessibility of DNA to RNA polymerase. Proteins also play a role in DNA replication and transcription, ensuring the accurate duplication and expression of genetic information.
Applications in Biotechnology, Proteins and nucleic acids venn diagram
The understanding of proteins and nucleic acids has led to significant advancements in biotechnology. Proteins are used in the development of drugs, diagnostics, and therapeutic agents. For example, monoclonal antibodies, which are engineered proteins, are used to target and neutralize specific proteins involved in diseases such as cancer and autoimmune disorders.
Nucleic acids are used in genetic engineering and gene therapy. Recombinant DNA technology allows scientists to manipulate and insert specific genes into organisms, enabling the production of proteins for therapeutic purposes. Gene therapy involves the use of nucleic acids to treat genetic diseases by introducing functional copies of genes that are defective or missing.
Essential Questionnaire: Proteins And Nucleic Acids Venn Diagram
What are the key differences between proteins and nucleic acids?
Proteins are composed of amino acids and primarily serve structural and functional roles, while nucleic acids are composed of nucleotides and carry genetic information.
How do proteins interact with nucleic acids?
Proteins can bind to specific sequences on nucleic acids, regulating gene expression and facilitating DNA replication and transcription.
What are some examples of proteins that interact with nucleic acids?
Transcription factors, polymerases, and histones are examples of proteins that play crucial roles in nucleic acid metabolism.